how many cells produced in mitosis|mitosis / cell division : Tuguegarao Metaphase, in mitosis and meiosis, the stage of cell division characterized by . Stardew Valley is an open-ended country-life RPG! You’ve inherited your grandfather’s old farm plot in Stardew Valley. Armed with hand-me-down tools and a few coins, you set out to begin your new life. Can you learn to live off the land and turn these overgrown fields into a thriving home? It won’t be easy.
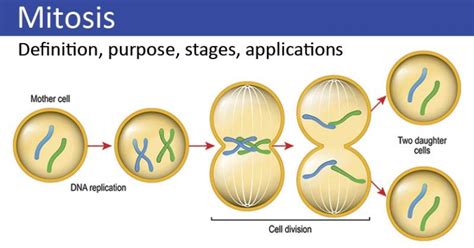
how many cells produced in mitosis,Mitosis is the division of a cell into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Meiosis is the division of a germ cell into four sex cells (e.g. egg or sperm), each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell.Mitosis begins at prophase with the thickening and coiling of the .
Metaphase, in mitosis and meiosis, the stage of cell division characterized by .Meiosis, division of a germ cell involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to .Anaphase, in mitosis and meiosis, the stage of cell division in which separated .During telophase, the chromosomes begin to decondense and the now-defunct .

nucleolus, spherical body within the nucleus of most eukaryotic cells, involved in the .mitosis / cell division nucleolus, spherical body within the nucleus of most eukaryotic cells, involved in the .how many cells produced in mitosis mitosis / cell division nucleolus, spherical body within the nucleus of most eukaryotic cells, involved in the .

The primary result of mitosis and cytokinesis is the transfer of a parent cell's genome into two daughter cells. The genome is composed of a number of chromosomes—complexes of tightly coiled DNA that contain genetic information vital for proper cell function. Because each resultant daughter cell should be genetically identical to the parent cell, the parent cell must make a copy of eac.
The primary result of mitosis and cytokinesis is the transfer of a parent cell's genome into two daughter cells. The genome is composed of a number of chromosomes—complexes of tightly coiled DNA that contain genetic information vital for proper cell function. Because each resultant daughter cell should be genetically identical to the parent cell, the parent cell must make a copy of eac.how many cells produced in mitosisThe primary result of mitosis and cytokinesis is the transfer of a parent cell's genome into two daughter cells. The genome is composed of a number of chromosomes—complexes of tightly coiled DNA that contain genetic information vital for proper cell function. Because each resultant daughter cell should be genetically identical to the parent cell, the parent cell must make a copy of eac.There are two ways cell division can happen in humans and most other animals, called mitosis and meiosis. When a cell divides by way of mitosis, it produces two clones of itself, each with the same number of .
The purpose of mitosis is to produce more cells. After the first round of mitosis, there are only two cells. These cells both undergo .
Cells with too few or too many chromosomes usually don’t function well: they may not survive, or they may even cause cancer. So, when cells undergo mitosis, they don’t just divide their DNA at random and toss it .
The five phases of mitosis and cell division tightly coordinate the movements of hundreds of proteins. . As the two daughter DNA strands are produced from the . During .Mitosis is a process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells that occurs when a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. During cell division, mitosis refers.The cell cycle. In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: interphase and mitosis (or the mitotic (M) phase). Interphase is the longest part of the .
how many cells produced in mitosis|mitosis / cell division
PH0 · mitosis / cell division
PH1 · The cell cycle and mitosis review (article)
PH2 · The Cell Cycle and Mitosis – Fundamentals of Cell Biology
PH3 · Phases of mitosis
PH4 · Mitosis (article)
PH5 · Mitosis
PH6 · Cell Division: Stages of Mitosis
PH7 · 25.1: Cell division: Mitosis